Wasp stings quite often, particularly during the warmer months of the year when people are outside for a longer period.
Also, their stings can be uncomfortable and irritating. However, most people heal rapidly and without any health complications.
Wasps, honey bees, and hornets have a stinger for self-defense, which they use while they feel they are surrounded by danger.
Important Note: If you're tired of pests and want a reliable solution, then you should definitely consider seeking help from a professional pest control company. DIY solutions can be effective, but if you're dealing with a significant pest infestation, you don't want to rely solely on DIY methods. Pest control companies typically don't charge huge fees. You can fill out this form to receive free quotes from the top local pest control companies, and compare the quotes and see for yourself. Then, finally, your pest problems will be eliminated for good.
In this article, I’ve attempted to cover all questions related to wasps and in what situation a wasp would be able to sting you.
Do Wasps Sting or Bite?
Wasps sting, they don’t bite. While they may also bite people if they feel threatened, their primary method of defense is stinging.
When a wasp stings, it inserts its stinger into the skin and releases venom into the surrounding tissue, causing pain, inflammation, and swelling.
What Does a Wasp Sting Look Like?
A wasp sting usually causes a raised welt or bump at the site of the sting.
The skin around the sting may be red and swollen, and there may be a tiny white mark in the middle where the stinger penetrated the skin.
The pain can be quite intense, and there may be some itching and burning as well.
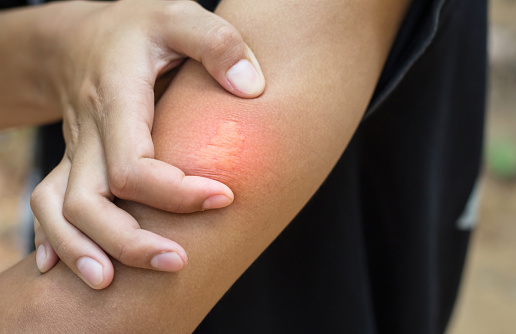
Most Common Symptoms of Wasps Sting
A wasp sting can be a painful and frightening experience, but knowing the symptoms can help you seek treatment quickly.
- Pain or burning sensation at the site of the sting.
- Redness and swelling around the sting.
- Itching or tingling at the sting site.
- A raised welt or bump at the site of the sting.
- Nausea and vomiting (in some cases).
- Dizziness or fainting (in some cases).
- Difficulty breathing or swallowing (in severe cases).
- Hives or rash (in some cases).
Most people will experience mild to moderate symptoms that go away within a day or two.
However, some people may have a more severe reaction to a wasp sting, which could be life-threatening if not treated promptly.
Treatment for Wasps Sting
If you’ve been stung by a wasp, there are several steps you can take to alleviate the pain and discomfort. Here are some common treatments for wasp stings:
- Remove the stinger if it’s still in your skin.
- Wash the affected area with soap and water.
- Apply a cold compress or ice pack to reduce swelling and pain.
- Take over-the-counter pain relief medication such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen.
- Apply a topical cream or ointment to help relieve itching.
- Elevate the affected area if possible, to reduce swelling.
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids.
- Rest and avoid strenuous activity.
If you experience a severe allergic reaction to a wasp sting, including difficulty breathing or swallowing, rapid heartbeat, or swelling of the face or throat, seek medical attention immediately.
Severe reactions may require emergency treatment with epinephrine (adrenaline) or other medications.

Frequently Asked Questions About Wasps
Can All Wasps Sting You?
Every kind of wasp is capable of stinging; however, just the female wasps can sting.
Wasps usually sting when they are irritated or when they feel threatened. If wasps feel that you will hurt them or their nest, they will immediately sting you multiple times.
Will Wasps Sting for No Reason?
It may feel like that, but wasps do not sting you without any reason.
At the point when wasps attack, they sting humans as a self-defense mechanism. Wasps comprehend that people are a lot bigger and more powerful and are not a part of their food chain. To wasps, people are only a danger to their colony.
At the point when a wasp stings an individual, they do as such because they dread that they are in harm’s way.
Do Wasps Leave Stingers?
Unlike honey bees, wasps and hornets don’t usually leave stingers in place, but treatment for all kinds of stings is something very similar, Clean the infected site and apply ice to ease pain, irritation, and swelling.
Do Wasps Die When They Sting You?
No, wasps don’t simply die after they sting people.
Wasps have much smaller stingers that don’t stick to their target’s skin. Even if a wasp stings multiple times, it will still hold its stinger.

Can Wasps Sting at Night?
Wasps are quite active in the daytime.
Wasps normally don’t sting around during the evening time, and you’re safe to walk close to wasp nests during the evening time as long as their nest isn’t disturbed.
Can Wasps Sting More Than Once?
Unlike honey bees, wasps can sting multiple times since they don’t lose their stinger with their sting. They will likewise inject toxic venom into your skin with their sting.
Most wasp stings can be extremely painful. However, after the initial sting, they just cause minor irritation and swelling which can be treated at home.
Will Wasps Sting You to Death?
Indeed, however, it’s extremely unlikely! Like uncommon.
Here are the two different ways that wasps’ stings can be fatal: you can die because of getting stung multiple times, or you can die as the consequence of a severe allergic reaction to even one single sting.
Final Words
If you come across or stumble upon a wasp nest, you shouldn’t try to manage a wasp or hornet infestation all by yourself, as you might get stung by wasps multiple times.
Attacking honey bees, wasps, and hornet nests or colonies makes them feel threatened and angry as these all are extremely territorial.
It’s ideal to contact a pest control specialist if you have any kind of wasp or hornet infestation in or around your home.

